Digital Image Distribution and Networks
|
Outline |
Mind Map |
Digital Image Distribution and Networks
|
Outline |
Mind Map |
To begin this module,
CLICK
HERE.
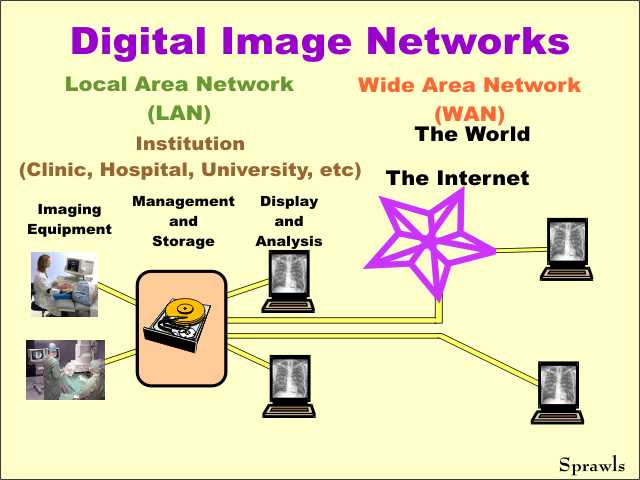 Networks
provide the connections among the various devices that makeup a digital
imaging system. Networks
provide the connections among the various devices that makeup a digital
imaging system.Local Area Networks (LANs) generally connect the imaging equipment, manage and storage devices, and displays within an institution. Wide Area Networks (WANs) provide connections with users outside of a local institution. The internet is a major component of many WANs. |
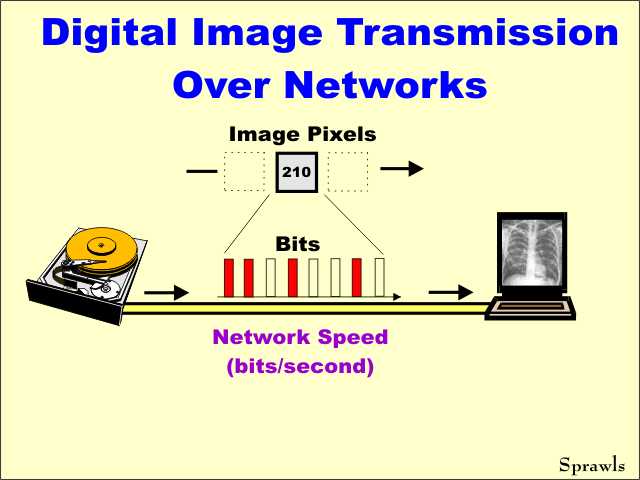 Digital
images are typically transmitted over networks as a series of pulses
(electrical, light, etc) that represent the individual bits. Digital
images are typically transmitted over networks as a series of pulses
(electrical, light, etc) that represent the individual bits.An important characteristic of a network is the speed with which it can transmit the bits (pulses). As we will soon see, this depends on the type of network. |
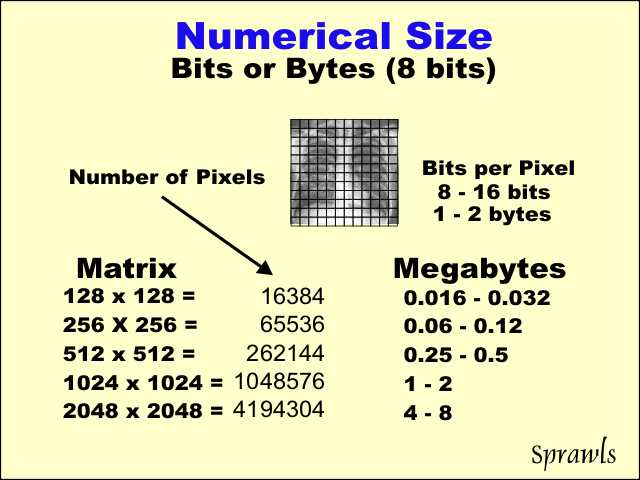 The
time required to transmit an image over a network depends on it's
numerical size (number of bits). The
time required to transmit an image over a network depends on it's
numerical size (number of bits).As we know, this depends on the number of pixels and the number of bits per pixel (the pixel bit depth). The matrix size is generally a characteristic of each specific imaging modality and covers a considerable range as shown here. |
 Image
transmission speed is typically fast and not a general problem within
LANs. Image
transmission speed is typically fast and not a general problem within
LANs.Speed is a major issue with WANs, especially with the network connections to the internet.
|
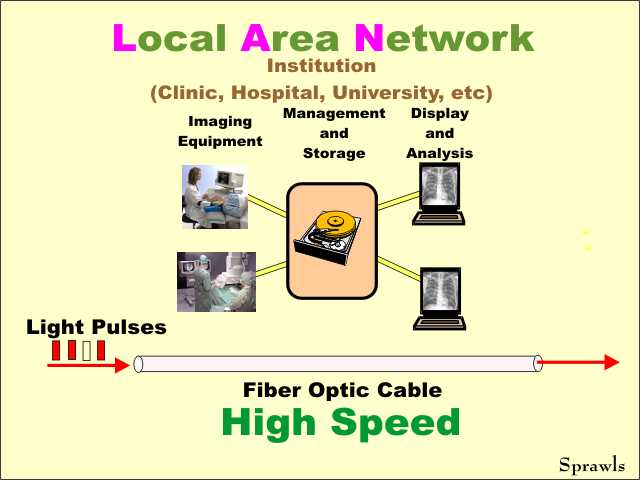 Many
LANs use fiber optic cable to transmit digital image data. Many
LANs use fiber optic cable to transmit digital image data.A fiber optic cable is made-up of transparent strands of glass fibers. Data is transmitted as a series of light pulses through the fibers. It is usually practical to install this type of network within an institution. An alternative is to use electronic cables for LANs. Many LANs (universities, airports, coffee shops, etc) also provide the capability for wireless connections to laptop computers, PDAs, etc. |
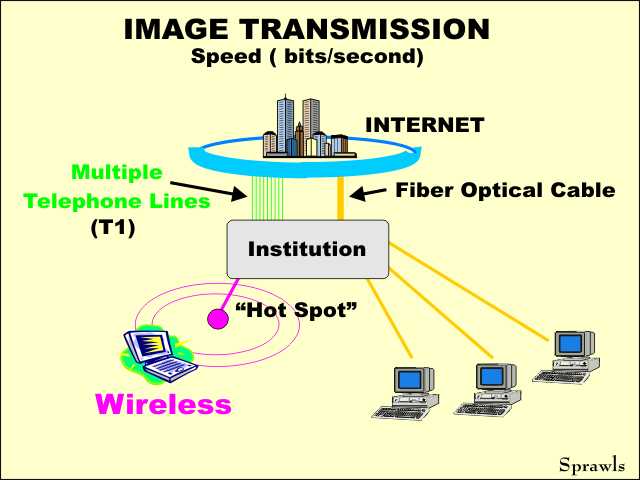 The
LAN in most institutions is usually connected to the internet "backbone"
with one of several types of high-speed network links. The
LAN in most institutions is usually connected to the internet "backbone"
with one of several types of high-speed network links.One approach, especially for institutions not located in major metropolitan areas where fiber optical cable connections are practical, is to lease a group of telephone lines. These can be made-up of different numbers of lines, depending on the required capacity (speed). A so-called T1 line is a common configuration. |
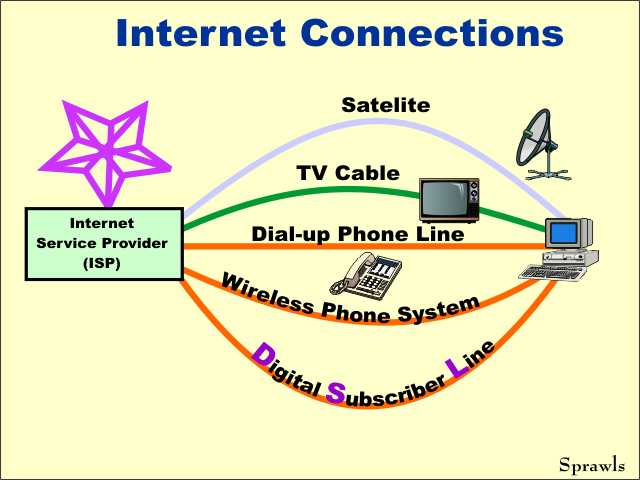 Individual
users must have a connection to the internet in order to receive images
(and for other functions like e-mail and viewing web pages). Individual
users must have a connection to the internet in order to receive images
(and for other functions like e-mail and viewing web pages).The Internet Service Provider (ISP) is the institution or commercial organization that has a high-speed connection to the internet "backbone" and then provides internet services to the individual users. There are a variety of methods than can be used to connect to the ISP. Each connection method has some limitations on speed as we are about to discover. |
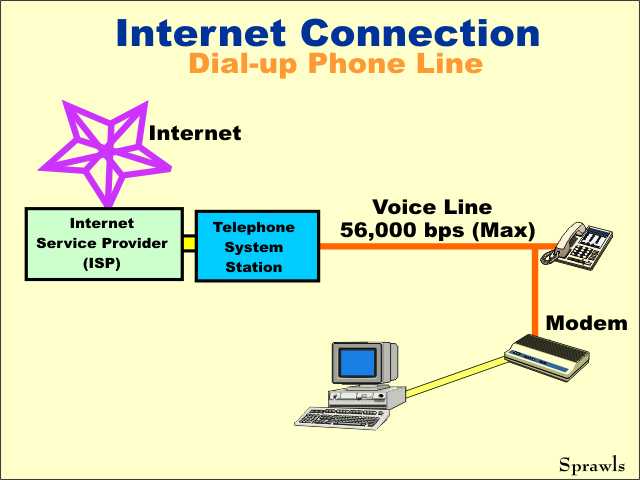 By
using a device called a modem, it is possible to connect computers to
conventional telephones and communicate with the ISP. By
using a device called a modem, it is possible to connect computers to
conventional telephones and communicate with the ISP.The modem converts the digital data (bits) into sound (tones) that will pass over the telephone line. The advantage of this type of connection is that telephone lines are available just about everywhere. The disadvantage is that conventional telephone circuits have a limit on how fast they can transmit data. That is usually a maximum of 56,000 bits per second, but is often much less because of the condition of the line, distance, etc. |
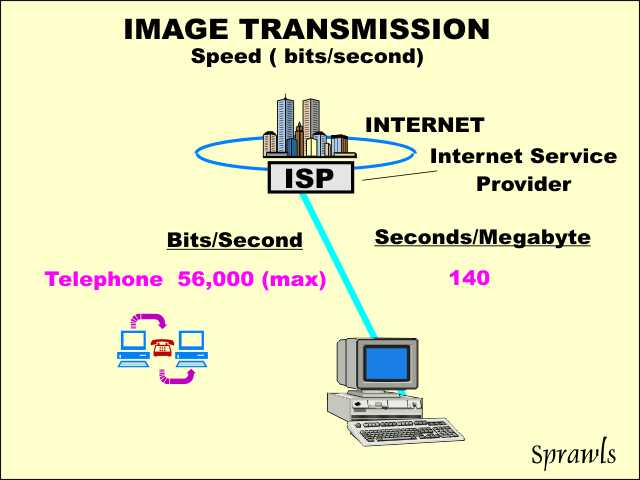 A
conventional telephone circuit would require over 140 seconds to
transmit one Megabyte of image data. A
conventional telephone circuit would require over 140 seconds to
transmit one Megabyte of image data. |
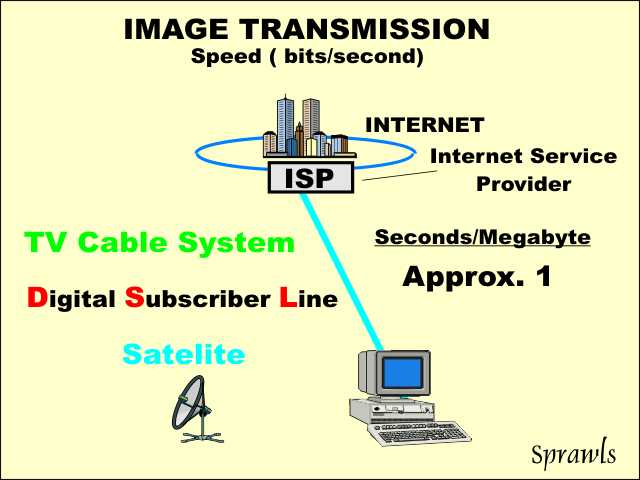 The
high-speed internet connections can typically transmit one Megabyte of
image data in approximately one second. The
high-speed internet connections can typically transmit one Megabyte of
image data in approximately one second. |
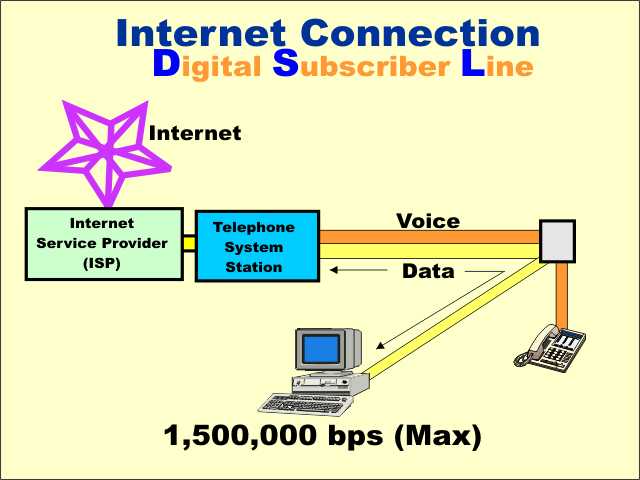 Digital
Subscriber Line (DSL) is a popular method for high-speed internet
connections. Digital
Subscriber Line (DSL) is a popular method for high-speed internet
connections.It is based on some special equipment that makes it possible to transmit the digital data, at high speeds, over the local telephone lines. It does not conflict with normal use of the telephone line for voice communications. One limitation is that the user must be relatively close (within three miles) of the telephone company facility. |
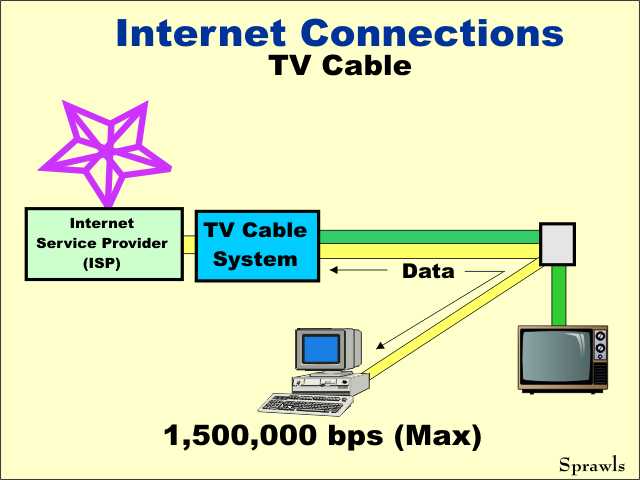 TV
cable systems have the capability to transmit data and information
at high rates. Note: A TV program is transmitted as 30 images each
second. TV
cable systems have the capability to transmit data and information
at high rates. Note: A TV program is transmitted as 30 images each
second.Therefore, TV cable companies can be high-speed internet service providers. Special equipment, usually called a Cable Modem, can be installed to separate the digital data from the TV signals. |
 There
are a variety of methods that can be used for connecting to the ISP. There
are a variety of methods that can be used for connecting to the ISP.Each method has speed limitations that must be considered. |
 Both
LANs and WANs play a role in transmitting and distributing digital
medical images. Both
LANs and WANs play a role in transmitting and distributing digital
medical images. |
|
To return to the beginning,
|
|
To return to the beginning,
|